Patterns and outcomes of chronic migraine treatment: insights from a two-month prospective study
Abstract
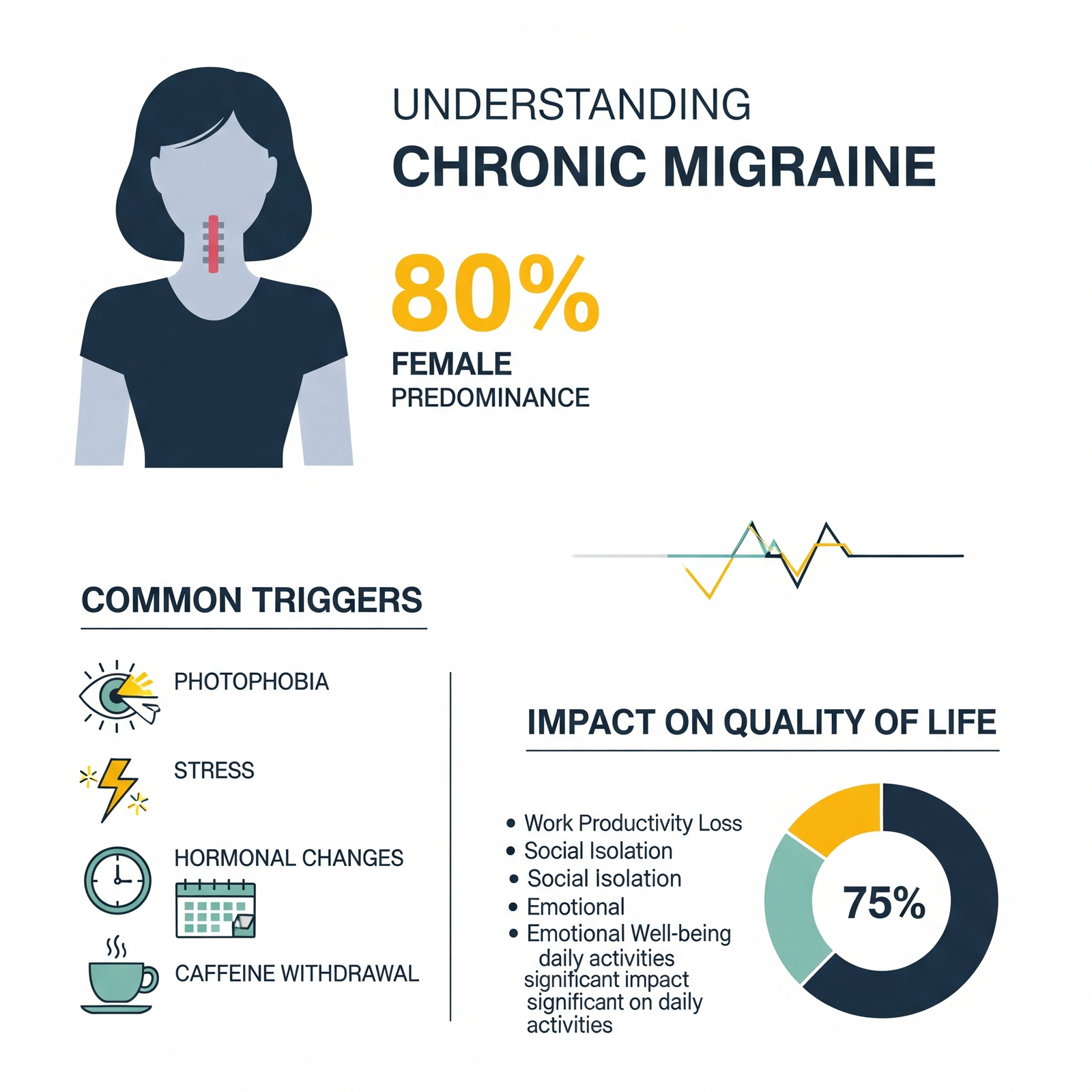
Background: Chronic migraine (CM) is a common and debilitating neurological condition that significantly impairs quality of life. Despite its prevalence, effective management remains underutilized. This study evaluated the effectiveness of various treatment strategies for CM and examined demographic patterns, common triggers, and their influence on treatment outcomes. Methods: A two-month prospective study was conducted at Crimson Hospital, Tilottama, Rupandehi, with 150 adult CM patients. Data on demographics, migraine characteristics, medication usage, and quality-of-life impacts were collected via structured patient profiles and verbal interviews. Statistical analyses, including paired t-tests, were used to evaluate treatment efficacy and explore relationships between variables. Results: The majority of participants were aged 31-45 years (53.3%) with a notable female predominance (80%). Common triggers included photophobia (62%) and stress (61.3%). Pharmacological interventions significantly reduced headache frequency from 5.78 to 2.37 attacks per month (p < 0.05). HIT-6 scores revealed a severe impact on quality of life in 36.7% of patients. NSAIDs and antidepressants were the most prescribed drug classes. Conclusions: Pharmacological treatments effectively reduced headache frequency and improved outcomes, but CM still profoundly impacts quality of life. Comprehensive management approaches, integrating pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies, are essential for optimal care. Future research should emphasize the long-term effects of treatments and enhanced patient education to improve care quality.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
KC, M. ., Gupta, S. ., Pandey, A. ., Aryal, A. ., Bhattarai, P. ., Musthfa, M. ., Bhandari, A. ., Kunwar, P. ., & Chaudhary, G. P. . (2025). Patterns and outcomes of chronic migraine treatment: insights from a two-month prospective study. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 16(3), 54–62. https://doi.org/10.26452/ijrps.v16i3.4791
Copyright (c) 2025 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.