development and evaluation of an oral quinine sulphate sustained release formulation for the management of visceral leishmaniasis
Abstract
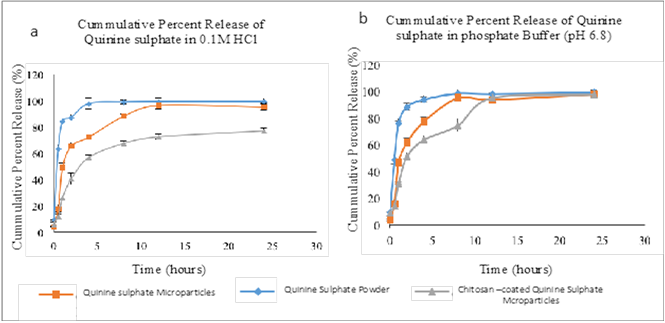
Background: Visceral Leishmaniasis is a systemic disease caused by the invasion of reticuloendothelial cells in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow by Leishmania spp. parasites. Current medications have numerous adverse effects and some resistance has been reported. Most treatments are administered parenterally, leading to non-compliance and treatment failure. This study aimed to develop an oral formulation of quinine sulfate to address these challenges.Methods: Quinine sulfate was encapsulated in hydroxypropylmethylcellulose using the spray-drying method and evaluated for particle size, zeta potential, drug content, entrapment efficiency, and in vitro release properties. In the in vivo study, laboratory mice infected with L. donovani promastigotes were treated for two weeks.Results: The average size of the quinine sulfate microparticles ranged from 2.6 to 14.2 µm, with an entrapment efficiency of 93%. Oral formulations effectively cleared parasites from the organs.Conclusion: Orally administered quinine sulfate efficiently cleared parasites from the blood of infected mice and resolved infections in their organs.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Allotey-Babington, G. L. ., Nettey, H. . ., Erskine , I. J. ., Mensah , A. A. ., Gyamera, N. K. O. . ., Goode, N. A. . ., Kumadoh, D. . ., & Asiedu-Gyekye, I. J. . . (2024). development and evaluation of an oral quinine sulphate sustained release formulation for the management of visceral leishmaniasis . International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 15(4), 48–55. https://doi.org/10.26452/ijrps.v15i4.4720
Copyright (c) 2024 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.