The secret of wetland: Marsilea quadrfolia as a promising green (wild) edible for health, hidden hunger and longevity from semiarid region
Abstract
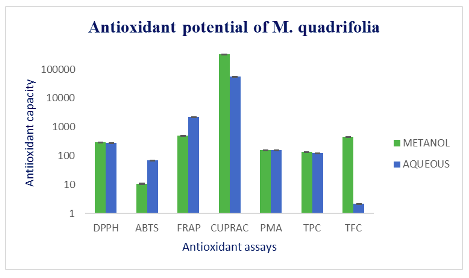
The future food security and hidden hunger are the major challenges which lead the developing countries for the exploration of wild edibles. Wild edibles have also been explored for their nutritional values which can potentially contribute to solving the issues such as malnutrition and livelihood in developing and rural communities of various parts of the world. This is first study to evaluate the nutritional values and phytochemical screening of semiarid populations of Marsilea spp. The nutritional analysis reveals carbohydrate (0.63 %), protein (4.20 %), fat (5.0 %), dietary fiber (8.6 %) and mineral content. the study also attempts various antioxidant assays such as DPPH, FRAP, ABTS, CUPRAC and PMA. The results show Marsilea is a very rich source of nutrition and minerals. It may help in livelihood development in developing and poor countries. This fern can also be utilized for fortification and developing the cultivation practice of Marsilea.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Rathore, R., & Solanki, H. (2024). The secret of wetland: Marsilea quadrfolia as a promising green (wild) edible for health, hidden hunger and longevity from semiarid region. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 15(3), 59–67. https://doi.org/10.26452/ijrps.v15i3.4696
Copyright (c) 2024 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.