Abstract
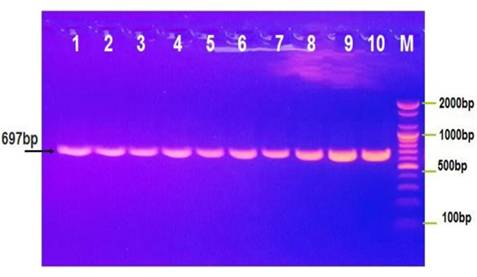
This study had studied the prevalence of some virulence genes which were carried by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients affected by active chronic otitis media (COM) in Ad-Diwaniyah teaching hospital, Iraq. Fifty samples were taken from affected patients and submitted to culture on media for enrichment then submitted to extraction of DNA by using of 16S rRNA gene in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test. Moreover, Phylogenetic analysis tree of DNA (sequencing methods) confirmed the results. A summarized results included 38/50 (76%) of total cases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, virulence genes included a toxic gene (84.2%), exoS gene (63.2%) and OprI gene (47.4%). The results also showed the multiple alignment analysis of sequencing similarity in 16S rRNA gene nucleotide sequences. It has been concluded that active COM may be more complicated due to virulence genes that carried by Pseudomonas aeruginosa; these virulence genes make the infection more difficult to be treated.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Kassim R. Dekhil. (2023). Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from active chronic otitis media. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 8(3), 389–396. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4591
Copyright (c) 2017 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.