Abstract
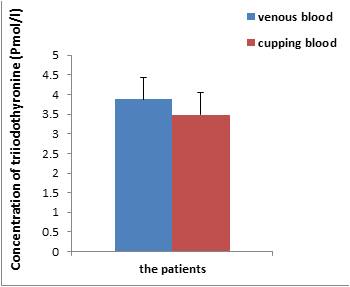
Due to the side effects of chemotherapy, some practitioners have reverted to the use of traditional medicine as complementary therapy. Several clinical studies have considered the effectiveness of cupping therapy to alleviate several diseases such as the widespread hypertension illness. The purpose of this study is to investigate the impact of cupping on blood, biochemical and hormonal indicators of hypertensive patients. Thirty voluntary male patients (45- 55 years) were chosen. Blood of pre-cupping (PC) and of cupping (CU) was obtained in order to measure blood constituents and biochemical variables. Results showed a significant increase in the concentration of blood cholesterol of CU patients compared with those of PC. The levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), triglycerides and glucose did not indicate any significant differences between the two groups. Concerning nitrogenous compounds, similarity was recorded in the level of total proteins, albumin and creatinine between the PC and the CU groups, while the urea level showed a clear decrease in CU individuals. On the other hand, the study showed a significant reduction in the levels of white blood cells, red blood cells, hemoglobin and platelets of CU blood. Concerning CU hormones, there was a significant decrease in the concentration of T3 and TSH, but T4 was significantly higher, while no significant change was observed in cortisol level. Cupping may help to reduce systolic pressure and cholesterol from the blood. This process may participate in reducing atherosclerosis, which could facilitate blood flow and reduce pressure on the heart, leading to the relaxation of patients.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Samia benzazia, Cherif abdennour, & Samia medjekane. (2023). Blood biomarkers of hypertensive patients participated in cupping therapy. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 8(3), 345–351. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4585
Copyright (c) 2017 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.