Abstract
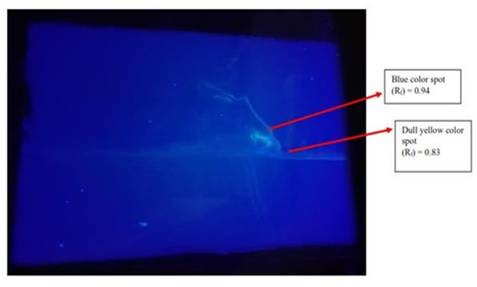
α-amylase hydrolyses starch into maltose, and cholesterol esterase hydrolyzes cholesterol ester into cholesterol and fatty acids in the lumen of small intestine. Regulated inhibition of the above cited enzymes can effectively control diabetes mellitus and associated cardiovascular diseases. In the above cited context, Nigella sativa (Black cumin) seeds were investigated for in vitro amylase and cholesterol esterase inhibitory properties. The amylase and cholesterol esterase inhibitory activities of hot water extract [HWE] (96.4±1.5% & 90±2.5%, respectively) and organic solvent extract [OSE] (98.1±0.5% & 96.6±1.2%, respectively) were found to be satisfactory. Appreciable amount of total phenolic content (TPC) and total flavonoid content (TFC) was observed in both the extracts. The thin layer chromatography (TLC) analysis of HWE has recorded an Rf value of 0.94 which established the presence of polyphenols. The purified polyphenol eluate by 3D preparative thin layer chromatography (PTLC) has recorded a moderate α-amylase (46.7±3.2%) and cholesterol esterase (32.6±1.7%) inhibitory activities. The polyphenols coated with cotton fabric, and stainless steel implant possessed noteworthy α-amylase and cholesterol esterase inhibitory activities has revealed the promising use of Nigella sativa in the healthcare industry to treat diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
q, S. T., Seetha Lakshmi S, Archana K, Aishwarya M, Divya S, Kumaresan K, Stephen Raphael V, Muthukumaran V, & Krishnaveni V. (2023). Evaluation of in vitro cholesterol esterase and α-amylase inhibitory activities of purified polyphenols from Nigella sativa seeds. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 8(3), 330–338. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4583
Copyright (c) 2017 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.