Abstract
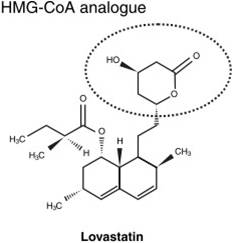
Lovastatin is a statin drug that blocks the body’s synthesis of cholesterol and is administered especiall y to individuals at risk of heart disease. Categorized as a Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) Class II drugs, lovastatin demonstrates low solubility and bioavailability. This review focuses on the importance of lovastatin and the obstacles during its administration. The history of statins from the discovery until they become one of the successful cholesterol-lowering agents to prevent complications and fatality especially related to coronary heart disease has been outlined along with their recent applicability in neurodegenerative diseases. Due to the respective physicochemical characters of the statins, they pose several challenges related to their effective administration to the patients. The aqueous solubility is the main issue related to their poor bioavailability. Besides that, other solubility and bioavailability enhancement approaches were discussed systemically. Finally, this review suggests current advanced technologies employed in order to provide effective and competent utilization of the drug.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Zolkiflee NF, Meor Mohd Affandi MMR, & Majeed ABA. (2023). Lovastatin: history, physicochemistry, pharmacokinetics and enhanced solubility. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 8(1), 90–102. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4541
Copyright (c) 2017 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.