Abstract
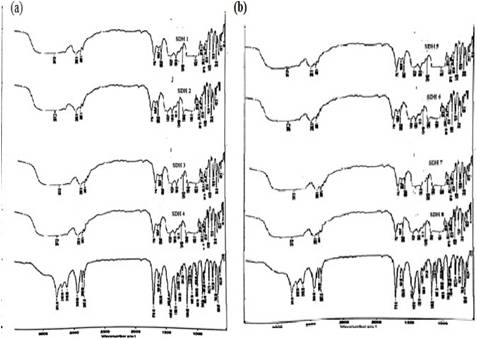
The scope of this study was to analyse the effect of polymeric precipitation inhibitor on in-vitro dissolution of Meloxicam which is a weak acid, water- insoluble and a crystalline compound. Meloxicam is used to treat pain or inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis. HPMC was used as polymeric precipitation inhibitor. Solvent evaporation method was employed to formulate solid dispersions with and without polymeric precipitation inhibitor. IR spectra suggested that there were no interactions between drug and polymers used in the study. DSC thermograms indicated that the drug was completely miscible with the molten carrier. Amorphization of the drug in the solid dispersion was established by a reduction in the enthalpy of drug melting in solid dispersion versus pure drug. The drug crystallinity in the solid dispersion was found to be reduced from X-ray Diffraction analysis. SEM analysis showed that Meloxicam exhibited irregular crystals, but the surface morphology of solid dispersions was smooth. Formulated solid dispersions showed increased solubility than the pure drug. Meloxicam solid dispersions with HPMC exhibited less precipitation rate compared to the Meloxicam solid dispersions without HPMC. Increase in the dissolution was attributed to the decrease in crystallinity of the drug and inhibition of drug precipitation. Thus, dissolution of Meloxicam can be enhanced by formulating solid dispersion using polymeric precipitation inhibitors.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Karnati V Chandana, Gowda DV, Vishal Gupta N, Praveen Sivadasu, & Manjunath M. (2018). Influence of polymeric precipitation inhibitors on dissolution behaviour of Meloxicam. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 9(4), 1179–1185. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4438
Copyright (c) 2018 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.