Abstract
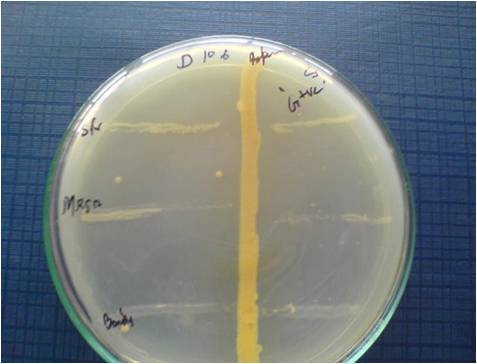
Immobilization of the whole cell offers high metabolic activity and Productivity. It is one of the key methods for the improvement of microbial strains producing bioactive compounds. In the present study, 18 actinomycete isolates were isolated from garden soil and screened regard with their potential against both gram-positive and negative bacteria including MRSA. Among the 18 strains, KUA06 showed good activity and they were characterized by macroscopically and microscopically. The promising isolate KUA06 were cultivated in liquid culture medium and immobilized with sodium alginate. The antibacterial compound was extracted by solvent extraction technique. Comparative studies on the total antibiotic sensitivity of the free cells and immobilized cells showed that the immobilized cells were effective against test pathogens; 25 mm against medically important organisms. Further, we concluded that the isolate immobilized KUA06 are more efficient for antibiotic synthesis against multidrug pathogens.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Juby TR, & Usha R. (2018). Immobilization of cells using Sodium alginate for enhanced productivity of antimicrobial compound. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 9(4), 1002–1007. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4402
Copyright (c) 2018 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.