Abstract
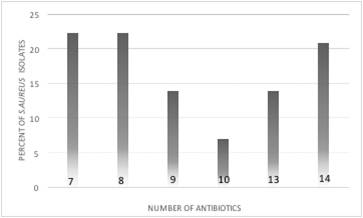
The present study was targeted to examine the prevalence of multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus, which has been carried out in Misan, Iraq at a local hospital from February 2016 to January 2017. A hundred and eighty ear swabs have been obtained from patients with ear infections with or without discharges. Culturing and identifying the causative agents, as well as the antibiotic sensitivity profile, have been done on the specimens. Swabs were collected under sterile conditions and instantly transferred to the laboratory sealed in brain heart broth tubes. The initial isolation was done on selective media to S. aureus (mannitol salt agar) at a temperature of 37°C for 24 - 48 hours and then the biochemical tests and identification were done in accordance with the standard monotonous techniques. Antibiotic susceptibility tests were done by the disk diffusion method. A hundred and forty-four isolates diagnosed with Staphylococcus aureus and eighteen isolates as other bacteria. S.aureus isolates tested for antibiotic susceptibility showed high resistance to ampicillin, carbenicillin and amoxicillin, mild resistance to co-trimoxazole and were susceptible to norfloxacin, rifampicin, and ciprofloxacin. Additionally, S.aureus isolates showed multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR). The MAR index of the isolates found to range between 0.35 and 0.7. In conclusion, an ear infection is mostly caused by Staphylococcus aureus and most of these isolates showed a high level of antibiotics resistance, which eventually may lead to too many health-related consequences in Misan, Southern Iraq and expose the needs for further studies to lessen the resistance to antibiotics.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Munaf Aal-Aaboda, & Mohammed R. Al-Notazy. (2023). Antimicrobial susceptibility of clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolated from patients with an ear infection in Misan. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 9(3), 900–905. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4369
Copyright (c) 2018 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.