Abstract
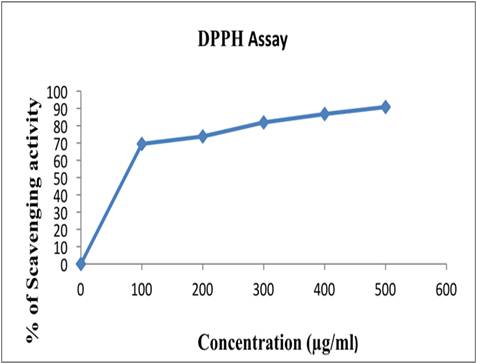
Seaweeds are the most important source of sulphated polysaccharides. These sulphated polysaccharides exhibit potent therapeutic properties. Fucoidan is a complex sulphated polysaccharide found in many species of brown algae. In the present study, fucoidan was extracted from brown seaweed, Sargassum wightii via different procedures: alcohol extraction, hot buffer extraction, hot water extraction and acid extraction. Through the study, it was found that extraction with hot buffer results in the maximum yield (7.3%) of the polysaccharide. Measurement of fucose and sulphate content revealed that the extracted polysaccharide showed characteristics of fucoidan. The results revealed that the yield and composition of fucoidan are dependent on extraction methodology. Fucose and sulphate-rich crude fucoidan were then subjected to 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), radical scavenging activity, using ascorbic acid as standard and it showed higher free radical scavenging activity in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 133 µg/ml. Thus fucoidan can be exploited as natural antioxidants for protection against oxidative stress which is found to be the cause for the development of several diseases.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Sharmila G, Anna Sheba L, & Ilakkia A. (2023). Determination of in vitro antioxidant activity of crude fucoidan extracted from Sargassum wightii by different methods. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 9(3), 868–873. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4363
Copyright (c) 2018 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.