Abstract
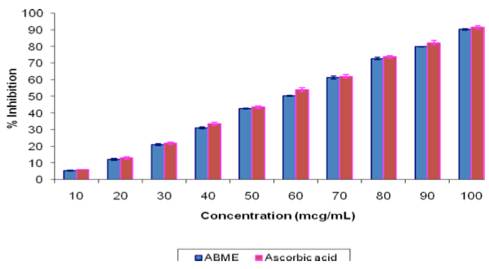
The study aimed to carry out the in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the methanolic extract of aerial parts of Alternanthera bettzickiana (ABME). ABME showed its ability to scavenge the free radicals in a concentration-dependent manner. The plant extract (100 mg) yielded 92.6±0.13mg/ml gallic acid-equivalent phenolic content and 280.5±0.12 mg/ml quercetin-equivalent flavonoid content. ABME showed total antioxidant activity with a Trolox equivalent antioxidant concentration (TEAC) value of 0.77±0.03. The IC50 values for scavenging of free radicals were 292.578μg/ml, 212.582 μg/ml, 146.1 μg/ml and 434.9μg/ml for DPPH, hydroxyl, superoxide and nitric oxide respectively. The antimicrobial activity was tested against strains of Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger. ABME was found to be effective against these tested organisms. The present study provides evidence that aerial parts of Alternanthera bettzickiana are a potential source of natural antioxidants with antimicrobial properties.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Ramakrishnan Padmini, Chandragiri Janakiraman Thirupurasundari, Subramania Bharathiraja, & Sivasithambaram Niranjali Devaraj. (2023). Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of methanolic extract of aerial parts of Alternanthera bettizickiana. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 9(3), 834–841. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4357
Copyright (c) 2018 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.