Abstract
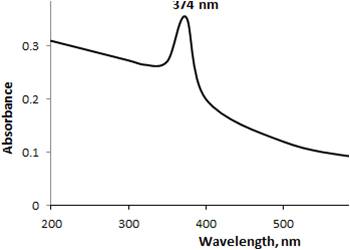
Seeds and sprouts of Vigna radiata (VR), commonly known as Mung bean, is a nutritionally potent common food. Though the seeds and sprouts of VR are not traditionally used as folklore medicine, various pharmacological activities are evaluated scientifically. The present study aims to Synthesize and characterize Zinc oxide nanoparticles from sprouts of VR and compare its free radical scavenging potency against an ethanolic extract of Vigna radiata (VR) and its sprouts (VRS). Zinc oxide nanoparticle from VRS is synthesized and characterized by UV, FTIR spectroscopy and SEM. The free radical scavenging potency of the synthesized nanoparticle, VR, VRS is evaluated by ABTS radical scavenging assay and reducing potential. UV, FTIR and SEM image of synthesized Zinc oxide nanoparticle reflects the morphology of nanoparticle. In In-vitro free radical scavenging activity, ZnO Nanoparticle does not exhibits reducing potential activity. ABTS radical scavenging activity of VRS is significantly better than that of VR and ZnO Nanoparticle (p<0.01). In conclusion, ethanolic extract of Vigna radiata sprouts is a potent free radical scavenger than that of ethanolic extract of Vigna radiata and Zinc oxide nanoparticle synthesized from Vigna radiata sprouts.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Annapoorani B, Gayathri K, Sangeetha R, & Orenbemo ONO. (2023). Comparative study on the free radical scavenging potency of Vigna radiate sprouts and its zinc oxide nanoparticle. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 9(3), 801–806. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4350
Copyright (c) 2018 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.