Abstract
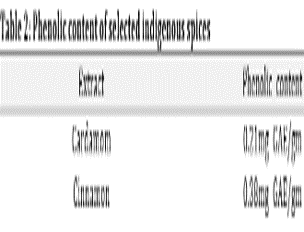
The necessity of culinary herbs in human life, spices plays a major role as they are versatile in feature. Indigenous spices, the spices which is cultivated and developed naturally in its own place (India). This current research was to compare and analyse the phytochemical and total phenolic content of indigenous spices. The major indigenous spices which we are using in day to day life such as Elletaria cardamomum (cardamom), Cinnamomum vernum (Cinnamon), Cuminum cyminum (Cumin), Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek), Coraindrum sativum (Corainder). The phytochemical analysis tests such as test for carbohydrates, flavanoids, alkaloids and terpenoids were done using the extract of above mentioned spices. The phenolic content was measured using folin ciolcaletu’s reagent. The phytochemicals such as phylobattaninns, carbohydrates, flavanoids, alkaloids and terpenoids were present in the collected indigenous spices. The comparative phytochemical analysis and total phenolic content of selected indigenous spices was found and its uses were compared.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.