Abstract
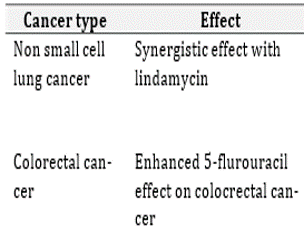
Chloroquine is a prototype antimalarial drug used to prevent and treat malaria, amebiasis and other autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. The drug acts as an autophagy inhibitor were autophagy is a self-destructive process which is needed to balance sources of energy at developmental process and in response to nutrient deprivation. New studies have shown the crucial role of chloroquine in cancer treatment and is been extensively used as a monotherapy or adjunct therapy in various types of cancer. This review summarizes the role of chloroquine and its action as an autophagy inhibitor in cancer treatment and also the various safety issues concerning with the same.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.