Abstract
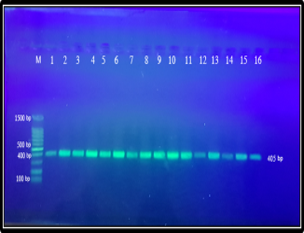
The main goal of the current study is to isolate and diagnose of Streptococcus agalactiae by using the diagnostic 16 SrRNA gene. S. agalactiae was isolated from 850 samples including (425) vaginal swabs, (425) rectal swabs and identified by studying the morphological characteristics of colonies on culture, microscopic characteristics of bacterial cells, biochemical methods, Vitek 2 system, API-20 Strep, and then confirmed the identification by detection of 16SrRNA gene by Polymerase Chain reaction (PCR) followed by DNA Sequence analysis for this gene. A total of 16 isolates of S.agalactiae were isolated from 12 (2.82%) vaginal swabs, 4 (0.99%) rectal swabs, and 16SrRNA was detected in 100% of the S.agalactiae isolates.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.