Abstract
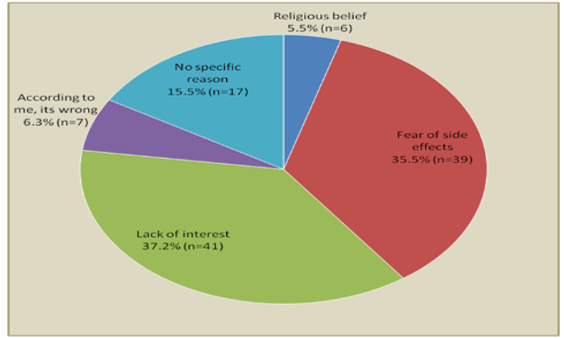
In the Indian society, various factors other than mere knowledge have shown to have a more significant impact over contraceptive usage and choice such as educational levels of women, marital duration, cultural and social factors, and exposure to mass media. This study focuses on assessing the knowledge, attitude and practices (KAP) of contraceptive use among married women. A cross-sectional study was conducted among married women aged between 18 to 49 years attending a tertiary care hospital in the city of Chennai from June to September 2018. A total of 146 women were interviewed, and the KAP parameters were assessed using a pretested structured questionnaire. Though 97.9% (n=143) of the women in this study had knowledge about some form of contraception, only 24.7% (n=36) practiced them. Among the users (n=36), the decision to adopt contraception was made by the husband in 69.4% (n=25). Among the non-users (n=110), the major reasons for not practicing contraception were lack of interest in 37.2%(n=41) and fear of side effects in 35.5% (n=39). This study demonstrates a significant gap between the knowledge and practice of contraceptives in our population. Improving doctor-patient relationship and encouraging a positive attitude of the husband towards contraception are the key factors in promoting adoption of the contraceptive practices.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.