Abstract
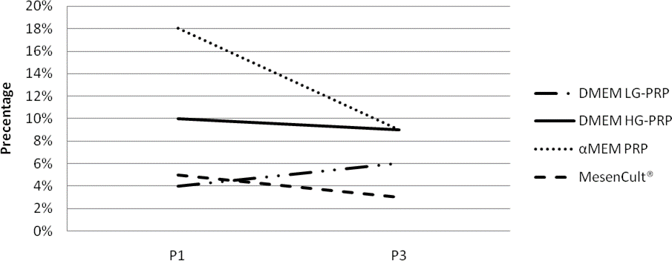
Previous studies used fetal bovine serum (FBS) containing medium for umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cell culture. Xenoproteins in FBS may be incorporated into the cultured cells and cause immune rejection, when the cells are used in patients. Therefore, the aim of this study was to compare propagation performance of umbilical cord derived stem cells that were cultured in various platelet rich plasma (PRP) containing media and FBS derivate containing commercial medium.This study was an in vitro analytical study on multiple harvest explant culture derived stem cells, which compared the stem cell population doubling time (PDT) of passage 1-3 cultures in human AB PRP containing media (low glucose and high glucose DMEM, and αMEM) compared to xenopretein containing commercial medium, MesenCult®. Overall, the lowest PDT was achieved by αMEM-PRP, and PDT in DMEM LG-PRP and αMEM PRP was comparable to those of MesenCult®. Features of cluster of differentiation (CD) expressions in P-1 suggest that the umbilical cord derived stem cells obtained from multiple harvest explant culture were not homogenous for MSCs. However, MSCs tended to become more homogenous with passages, especially for cells that were cultured in MesenCult®, followed by those cultured in αMEM-PRP. In conclusion, the best propagation performance of umbilical cord derived stem cells passage 1-3 cultures was achieved in PRP containing αMEM.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.