High Fat Diet and Low Dose Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Dyslipidaemia and Hepatic Damage in Rats
Abstract
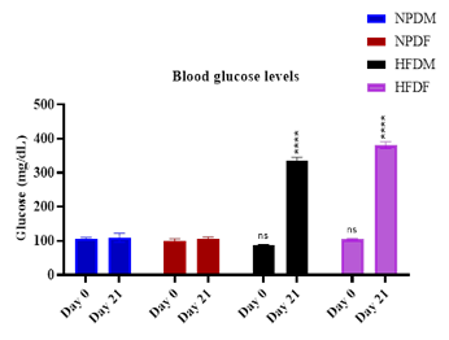
The objective of the present study was to validate a rat model of diabetic dyslipidaemia along with hepatic damage by High fat diet and low dose streptozotocin combination that resembles the natural history of metabolic syndrome in humans. Male and Female Sprague Dawley rats were divided into 2 groups. One group of rats fed with high fat diet and other group was fed with normal pellet diet for a period of 2 weeks followed by streptozotocin administration on 15th day. Body weight of the animals was measured on day 0, 14 and 21, also post 1 week of the streptozotocin administration the blood glucose, serum lipid, liver, kidney markers and insulin levels were measured. The high fat diet fed animals had exhibited a significant increase in body weight post two weeks of HFD feeding, but the body weight was reduced post 1 week of streptozotocin intervention due to metabolic disruption caused by STZ. The HFD group animals exhibited significant increase in blood glucose, serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL, VLDL. Similarly, a significant decrease in HDL and serum insulin levels were observed as compared to the NPD fed animals. Further the HFD group animals had shown significant elevation of the liver function enzymes such as ALT and ALP levels as compared to the NPD fed animals. The present study confirms the experimental induction of diabetic dyslipidaemia along with hepatic damage which serves as an ideal model for metabolic syndrome along with hepatic cirrhosis which would useful for evaluating the therapeutic agents against type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidaemia and hepatic cirrhosis.
Full text article
References
R Nall. An overview of diabetes types and treatments. Newsletter on Health. Medical News Today, 1(1):1–5, 2018.
M Asif. The prevention and control type-2 diabetes by changing lifestyle and dietary pattern. Journal of education and health promotion, 3, 2014.
V Rajadhyaksha. Managing diabetes patients in India: Is the future more bitter or less sweet? Perspectives in clinical research, 9(1):1, 2018.
A Kanno, S I Asahara, K Masuda, T Matsuda, M Kimura-Koyanagi, S Seino, and Y Kido. Compensatory hyperinsulinemia in high-fat diet-induced obese mice is associated with enhanced insulin translation in islets. Bio- chemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 458(3):681–686, 2015.
K Srinivasan, B Viswanad, L Asrat, C L Kaul, and P Ramarao. Combination of high-fat diet- fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacological research, 52(4):313–320, 2005.
M J Reed, K Meszaros, L J Entes, M D Claypool, J G Pinkett, T M Gadbois, and G M Reaven. A new rat model of type 2 diabetes: the fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rat. Metabolism-Clinical and Experimental, 49(11):51653–51662, 2000.
S Lenzen. The mechanisms of alloxan-and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia, 51(2):216–226, 2008.
M Trombetta, G Spiazzi, G Zoppini, and M Muggeo. type 2 diabetes and chronic liver disease in the Verona diabetes study. Alimentary pharmacology and therapeutics, 22:24–27, 2005.
K F Petersen, S Dufour, D Befroy, M Lehrke, R E Hendler, and G I Shulman. Reversal of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis, hepatic insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia by moderate weight reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, 54(3):603–608, 2005.
A Mandal, B Bhattarai, P Kafle, M Khalid, S K Jonnadula, J Lamicchane, and V Gayam. Elevated liver enzymes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cureus, 10(11), 2018.
S Hussain, M C Jamali, A Habib, M S Hussain, M Akhtar, and A K Najmi. Diabetic kidney disease: An overview of prevalence, risk factors, and biomarkers. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 9:2–6, 2021.
N Harita, T Hayashi, K K Sato, Y Nakamura, T Yoneda, G Endo, and H Kambe. Lower serum creatinine is a new risk factor of type 2 diabetes: the Kansai healthcare study. Diabetes care, 32(3):424–426, 2009.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.