Abstract
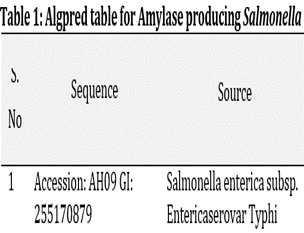
Allergies intolerance is a common problem worldwide. The major difficulties are related to the correct diagnosis of causes which is associated with amino acid sequences present in the epitope region of allergen. So there is a need to find out the factors causing allergies and allergens themselves. In the present study a bioinformatics tool is used to predict amino acid sequence and mast cell association with different integrated approaches. Internet databases for amylase producing bacteria were used in In-silico method to check the allergy for microorganism producing the extracellular enzyme. Amylase is an extra-cellular enzyme isolated from soil bacteria Salmonella species and Proteus vulgaris. It is very important in the pharmaceutical industry to check the allergenicity of any drug, protein or enzyme that be used in the treatment of diseases or food industries for various purpose. The aim of the present study is isolation and characterisation of extracellular enzyme produced from soil bacteria and to analyzed allergic response through AlgPred tool of bioinformatics. From results, it was concluded that the protein sequence of amylase did not contain any epitope, no hits for mast and blast which proved that it was not an allergen. So, bacterial isolates from the industrial soil are a good alternative source of enzyme production and may be used as an industrial level. Thus, from the results, it may be concluded that microbes from soil sample can be a good source of industrially important enzymes without any allergy.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.