Abstract
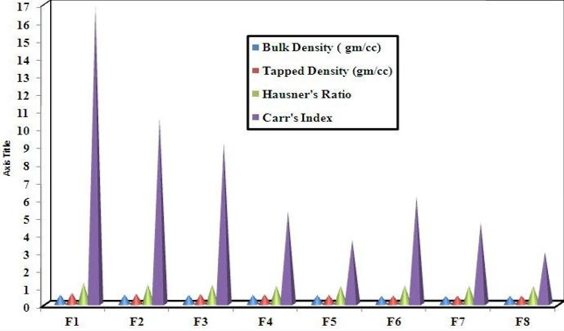
Hydrophilic swellable polymers are widely used to control the release of drugs from matrix formulations. The natural polymers are biodegradable and nontoxic, which hydrate and swell on contact with aqueous media. The present investigation is aimed to formulate the controlled release matrix granules of Amoxicillin trihydrate with different concentration of a plant derived gum, gum karaya, using no other varying parameter. Prepared granules were evaluated for different micrometrics properties like bulk density, tapped density, Hausner’s ratio, Carr’s index. The drug content and swelling behaviour were also investigated along with drug release kinetics. Percent swelling of the granules was 10-107.87 % in phosphate buffer pH-6.8. The drug release data from the granules were fitted in kinetic models of zero order, first order and Higuchi. The granules with 10-15% of gum karaya reveal the dominance of the highly swollen layer which controls the drug release from the granules. The findings lead to the conclusion that the matrix granules can be compressed to tablet to get a successful oral controlled release formulation.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.