Abstract
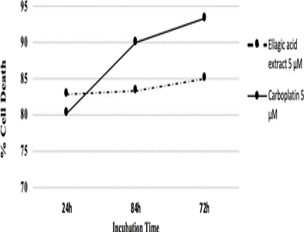
Recently, plant-derived compounds have been attracted increasable attention as alternative cancer remedies to enhance cancer prevention and healing, and as efficient antimicrobials, because of their low toxicity, low cost and fewer side effects. Ellagic acid (EA) is a natural phenolic constituent; previous studies have reported its antitumor properties when used in in vitro models. In this study, we have investigated the activity of a low concentration of EA against four different human cancer cell lines (SK-N-SH, Caov-3, SW-1088 and BxPC-3) which are very hard in the treatment and there is no available data about EA influence on them. Additionally, the effect of EA has assessed against (H. Pylori (Helicobacter pylori), P.aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeru- ginosa), A. tumefaciens: Agrobacterium tumefaciens (Rhizobium radiobacter) and E. herbicola: Enterobacter agglomerans (Erwiniaherbicola) and two are Gram-positive bacterium S. aureus (Staphylococcus aureus) and C. acnes (Cuti- bacterium acnes)) strains which are resistant to the antibiotics. The results suggest that EA may have a potential role as an adjunct therapy for neuroblastoma, ovarian, pancreatic and astrocytoma cancers, in addition to its activity as an antimicrobial agent as it has been proved in this study against H. pylori, P.aeruginosa, A. tumefaciens, E. herbicola, S. aureus and C. acnes strains.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.