Patient perspective regarding late termination of pregnancy at a tertiary care hospital
Abstract
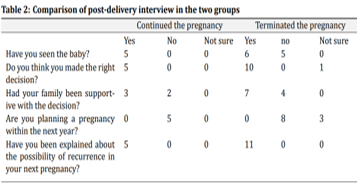
To arrive at an understanding about the view and attitudes of pregnant women regarding late termination of pregnancy after prenatal diagnosis of a severe fetal anomaly. A semi-structured questionnaire based prospective descriptive study was conducted from January 2022 to September 2022 in Obstetrics and Gynecology department of Saveetha Medical College and Hospital, Thandalam. 16 pregnant women with severe fetal anomalies detected after 23 weeks were included. All the women were counselled about the type and lethality of the anomaly including management option. Informed consent was obtained from all the patients and ethical approval was obtained. A total of 16 women with congenital anomalies in fetus detected after 23 weeks of gestation over 8 months of the study period were included in the study. All the participants were properly counselled and given adequate time to make the decision. Among which 11 decided to terminate the pregnancy and 5 continued. All 11 who opted for termination of pregnancy was joint decision by the family. 5 women continued their pregnancy. Reasons to continue the pregnancy were praying that baby will born normal (n=1), hoping that surgery can correct the abnormality (n=3) and wanting to see the baby (n=1). This study shows that women who are pregnant with serious fetal anomalies have a range of opinions and attitudes regarding termination. To compare with initial decision making larger follow-up studies will be necessary to see whether patient’s perspective changes over time.
References
L Govender and J Moodley. Late termination of pregnancy by intracardiac potassium chloride injection: 5 years’ experience at a tertiary referral centre. South African Medical Journal, 103(1):47–51, 2013.
Henry P David, L Herbert, Jean Friedman, Van Der, Marylis J Tak, and Sevilla. Abortion in Psychosocial Perspective: Trends in Transnational
Research, volume 97. Henry P David, New York, 1978. ASIN : B002WCDCPY.
A Gagnon, R D Wilson, and V M Allen. Evaluation of prenatally diagnosed structural congenital anomalies. J Obstet Gynaecol Can, 31(9):34307–34316, 2009.
T H Sasongko, Abd Razak Salmi, A R Zilfalil, B A Albar, M A Hussin, and Zam. Permissibility of prenatal diagnosis and abortion for fetuses
with severe genetic disorder: Type 1 spinal muscular atrophy. Annals of Saudi Medicine, 30(6):427–431, 2010.
S Ahmed, J M Green, and J Hewison. Attitudes towards prenatal diagnosis and termination of pregnancy for thalassaemia in pregnant Pakistani women in the North of England. Prenatal Diagnosis, 26(3):248–257, 2006.
S Ahmed, J Hewison, J M Green, H S Cuckle, J Hirst, and J G Thornton. Decisions about testing and termination of pregnancy for different fetal conditions: A qualitative study of European white and Pakistani mothers of affected children. Journal of Genetic Counseling, 17(6):560–572, 2008.
K Hunt, E France, S Ziebland, K Field, and S Wyke. My brain couldn’t move from planning a birth to planning a funeral: A qualitative
study of parents’ experiences of decision making after ending a pregnancy for fetal abnormality. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 46(8):1111–1121, 2009.
Acg Breeze, C C Lees, and A Kumar. Palliative care for prenatally diagnosed lethal fetal abnormality. Archives of Disease in Childhood -
Fetal and Neonatal Edition, 92(1):56–58, 2007.
A P Souka, V D Michalitsi, and H Skentou. Attitudes of pregnant women regarding termination of pregnancy for fetal abnormality. Prenatal Diagnosis, 30(10):977–980, 2010.
T Gammeltoft, T M Hang, N T Hiep, and N Hanh. Late term abortion for fetal anomaly: Vietnamese women’s experience. Reprod Health
Matters, 16(31):31373–31374, 2008.
L Dallaire, G Lortie, and De Rochers. Parental reaction and adaptability to prenatal diagnosis of fetal defect or genetic disease leading to
pregnancy interruption. Prenatal Diagnosis, 15(3):249–259, 1995.
Mca Mourik, J M Connor, and Ferguson-Smith Ma. The psychosocial sequelae of a second trimester termination of pregnancy for fetal
abnormality. Prenatal Diagnosis, 12(3):189–204, 1992.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.