Abstract
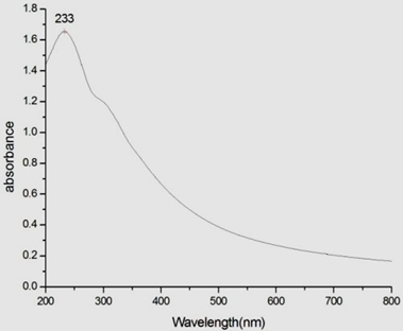
Graphene and graphene oxide (GO) layers have become a hotspot so far and have been actively investigated to build new composite materials. These novel nanomaterials have great potential in applications such as electro- chemical devices, energy storage catalysis, and adsorption of enzyme, cell imaging and drug delivery, as well as biosensors. In this project, we have synthesized graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) by chemical method and characterized with UV- Vis spectroscopy, FTIR, Raman spectroscopy and XRD. The antibacterial activity of GO and rGO aqueous dispersions toward selected microorganisms were compared. Colony counting method results show that GO has the highest antibacterial activities, followed by rGO under the same dispersion concentration.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.