Abstract
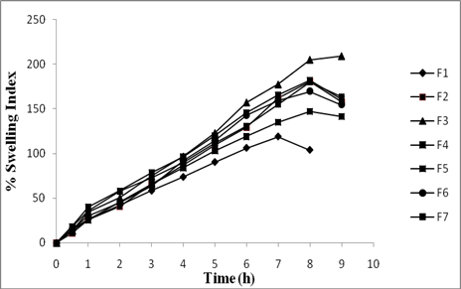
In the present investigation concern, the formulation and evaluation of bilayer floating tablet of diltiazem hydrochloride which after an oral administration increase gastric residence time, to increase the bioavailability. Diltiazem HCl is the Ca2+ channel blocker which used in ischemic heart disease and hypertension. It has a half-life of 3 – 4 h and bioavailability of 40%. Moreover, after administration of 60 mg of sustained release dose it required 3.9 h to reach peak plasma concentration. So to overcome these drawbacks it is advantageous to formulate bilayer floating tablet of diltiazem hydrochloride helps to increase bioavailability, decreases the frequency of administration and also to reach peak plasma concentration rapidly. Bilayer floating tablets comprised of two layers, immediate and control release layers. The immediate release layer is comprised of gas generating system sodium bicarbonate and citric acid, control release layer comprised of low density release retardant polymers like HPMC K4M, K15M, E50LV. The prepared powder blends were subjected to FT-IR for any interaction. The tablets were prepared by direct compression. First, the powder blends of controlled release layer was precompressed and then powder blends of immediate release layer was added. The tablets were evaluated for hardness, friability, drug content, floating lag time, total floating time, swelling index and in vitro drug release. In the present study, it was found that formulation F3 showed maximum release retardant capacity, F4, F5, F2 were next in sequence. The release data were fitted to various mathematical models such as Higuchi, first order and zero order to evaluate kinetics and mechanism of drug release, and it was and best fitted to first order and Higuchi's model. Stability studies revealed no significant changes.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.