Abstract
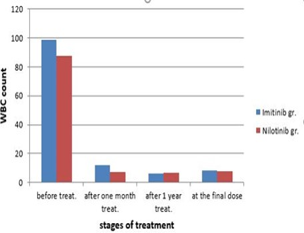
Chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) is one of the human fatalities caused by genetic mutation and chromosomal translocation, a BCR-ABL fusion gene and as a result, Philadelphia chromosome is formed. The irregular tyrosine kinase activity of the encoded protein by this gene causes the establishment of the disease. This study was conducted at the period from September 2016 to February 2017, 100 Iraqi CML patients were divided into two groups, first group of 50 patients were received Imatinib 400-800 mg/day, second group of another 50 patients were received 800 mg/day Nilotinib, WBC were microscopically counted using improved Neubauer ruled hemocytometer counting chamber. The results of WBC count in different disease duration and stages of treatment in the group of patients treated with Imatinib showed that highest WBC count was observed in newly diagnosed patients while there was a significant reduction in the WBC count after one month, after one year and final dose of treatment were 11.8, 6.4 and 8.1 respectively, on the other hand the results of WBC count in the group of patients treated with Nilotinib showed that the highest WBC count was observed in newly diagnosed patients 87.54 ± 8.71 whereas the WBC count after one month, one year and at the final dose of treatment were 7.3, 6.8, 7.9 respectively with significant reduction in the WBC count. The results of the CML patient’s distribution according to BCR-ABL gene analysis in the patient's group treated with Imatinib showed that high concentration in newly diagnosed patients 4.753 as compared with significant reduction with other stages of treatment after one month and after one year 0.94 and 0.09 respectively.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.