Abstract
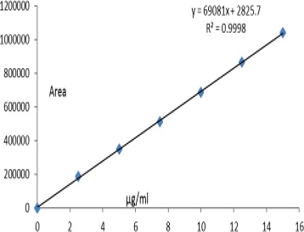
This research objective is for the development of a specific and simple method to trace Semaglutide presence in active pharmaceutical ingredient and pharmaceutical dosages. As part of a study on Semaglutide drug, solvents of HPLC grade waters HPLC instrument (Empower software) with PDA de- tector, ultrasonicator (Make: Labman) and pH meter (Make: Adwa) are used. The Method was optimized with mobile phase with a composition of buffer and solvent were of 60:40%v/v, flow maintained was 1.0ml/min, the injec- tion volume of 10µl, run time was 5min. All separations were performed with PDA detector and column used was Discovery C18 150 x 4.6mm, 5m. Results for the developed method are accurate and specific. The detection wavelength was 292 nm, the retention time for Semaglutide was 2.689min, linearity resulted with r2= 0.9998, % RSD for precision was 1.0; %mean recovery for accuracy was in the range of 99.73 to 100.29. This study report is for industrial application for determining Semaglutide presence in phar- maceutical ingredient and dosages.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.