Abstract
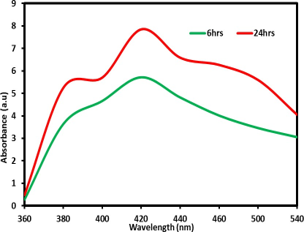
Biosynthesis of nanoparticles using microorganism is widely used in biological applications due to its eco-friendly nature and lower cost. The present study aimed to investigate the yeast, Candida albicans for the synthesis of nano cadmium sulfide is a semiconductor nanoparticle. The yeast synthesized nanoparticles tested for its spectroscopic and microscopic characters. The peak at 420 nm identified by UV-Vis spectrophotometer confirms the Cadmium sulfide (CdS) nanoparticles synthesis preliminarily. Further, the nanoparticles were characterized using X-ray diffraction assay, scanning electron microscope, and elemental dispersive analysis. Finally, the synthesized Cadmium sulfide (CdS) nanoparticles were tested for its antibacterial activity against disease-causing pathogens such as Salmonella typhi and Staphylococcus aureus. The maximum zone of inhibition shows 15mm at the concentration of 100µl of CdS nanoparticle. Thus a promising antibacterial activity of yeast mediated synthesized Cadmium sulfide (CdS) nanoparticles was described.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.