Abstract
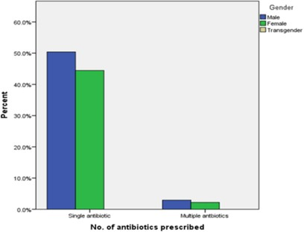
Extractions of molars are one of the frequently performed procedures in a dental clinic and it is associated with innumerable trans operative and post-operative complications, such as edema, trismus, localized alveolar osteitis, pain and surgical site infection. Some authors advocate the use of local and systemic antibiotics to reduce the incidence of these postoperative complications. Despite the risks of allergic reactions among some individuals, toxicity and the development of antibiotic resistant microorganisms, about 50% of dentists routinely prescribe the use of prophylactic antibiotics for this purpose, however the number of antibiotics prescribed vary among dental practitioners. A retrospective study was done among patients visiting the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery undergoing extraction of first and second mandibular molar and prescribed post-operative antibiotics. The number and group of antibiotics were noted, data were tabulated, and descriptive statistics were performed. Among 1909 patients, about 95% of the patients were prescribed single antibiotic post-extraction, and this was high among young adults, whereas multiple antibiotics were highly opted and prescribed for middle-aged adults.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.