Abstract
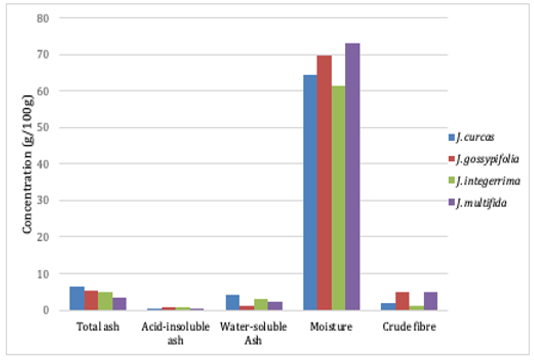
Jatropha is a large euphorbiaceous genus of tropical and subtropical distribution. Several species are used as traditional remedies for mouth sores, diarrhoea and skin diseases. This study aimed to estimate the amount of phenolic components in correlation to the antioxidant potential of the leaves of four Jatropha species acclimatised in Egypt. The plant material was subjected to determination of pharmacopoeial standards (ash values, moisture and crude fibre contents) and macronutrients (fat, protein and carbohydrates) for the establishment of reliable quality control criteria. Quantitation of phe- nolic compounds was performed spectrophotometrically and DPPH radical scavenging assay applied for in-vitro assessment of anti-oxidant activity. Quality control parameters differed among the analysed samples; total and water-soluble ash values were distinctly higher in Jatropha curcas and crude fibres in J. gossypifolia and J. multifida. Total phenolic, flavonoid and tannin contents were present in significant amounts in J. curcas, J. gossypifolia and J. multifida leaves; this could be partially correlated to their relatively moderate to appreciable anti-oxidant activities (IC50s 1.03, 1.7 and 1.26mg/mL, respectively). Meanwhile, the least amounts of phenolic compounds and lowest anti-oxidant potential were recorded for those of Jatropha integerrima. Results of proximate and macronutrient analyses could serve as suitable criteria for quality control of the investigated Jatropha species. The appreciable amounts of polyphenols detected in the leaves recommend intensive chemical and biological investigation of their component metabolites for further implementation in pharmaceutical products.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.