Abstract
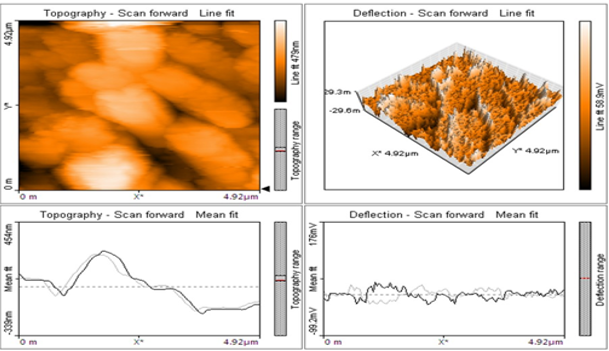
Rhizome extract of Acorus calamus was used for silver nanoparticles synthesis and examine the effect of physical and chemical parameters like time, pH, temperature and silver nitrate concentration in the process. Synthesized silver nanoparticles were characterized by UV–vis spectrophotometer shows the SPR band at 420-430 nm. It concluded that the optimum time, pH, temperature and silver nitrate concentration are 120 min, 6 or 7, 45°C and 1 mM silver nitrate concentration, respectively. Scanning Electron Microscope showed well dispersed spherical shaped nanoparticles with aggregation. EDAX confirmed that the presence of elemental silver in the reaction mixture observed at 3keV binding energy. TEM images confirmed that spherical shape nanoparticles with the size range of 2 – 40 nm. AFM image shows that the topography profile of synthesized silver nanoparticles and the observed size of nanoparticles is 30-55 nm. Antimicrobial activity of the rhizome mediated synthesized silver nanoparticles was performed by agar well diffusion method against gastrointestinal pathogens are bacteria Vibrio sp, Salmonella sp, Pseudomonas sp and Escherichia coli. The highest zone formation was observed against E. coli and Vibrio sp.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.