Abstract
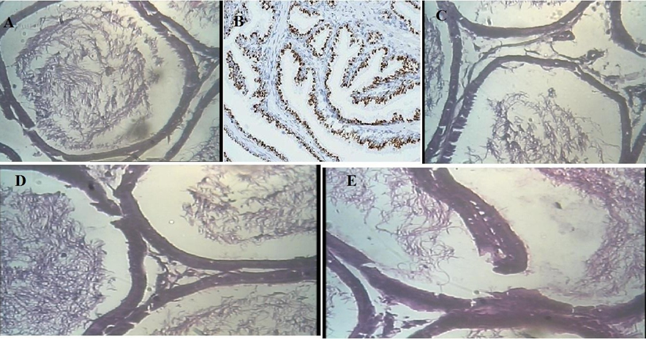
The aim of the present investigation is to establish the therapeutic potential of drugs affecting Renin Angiotensin System (RAS) on Testosterone induced benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in rats. We investigated whether RAS affecting drugs modulate on testosterone induced BPH in Rats. Animals were distributed in 5 groups (6 rats each). Group 1 receives only vehicles. Four other groups injected with Testosterone (3mg/kg, SC) to induce BPH, Group 2 was model group, Group 3 animals were treated with Enalapril (10mg/kg, IP), Group 4 animals were treated with Losartan (10mg/kg, IP), Group 5 animals were treated with Finasteride (5mg/kg, IP). The drugs were administered once a day for 21 days consecutively. Body weights were recorded before and after treatment. On 22nd day, blood samples were collected from the Retro-orbital plexus, centrifuged to obtain serum for determination of various parameters like Serum Testosterone level, Serum Prostate Specific Antigen, Serum Prostatic Acid Phosphatase, Serum Lactate Dehydrogenase. Then animals were sacrificed, prostates were weighed and histopathological studies of prostate were carried out. Effect of Enalapril and Losartan on contractility were examined on preparations of the isolated rat prostate gland. Enalapril and Losartan treatment showed significant inhibition of prostate enlargement, prevent the reduction in Serum Testosterone levels, reduced the level of Serum Prostate Specific Antigen, reduced the level of Serum Prostatic Acid Phosphatase, protection of histoarchitecture of prostate when compared with model group. These results suggest that Enalapril and Losartan has a definite inhibitory effect on BPH and might be an alternative medicine for treatment of human BPH.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.