Abstract
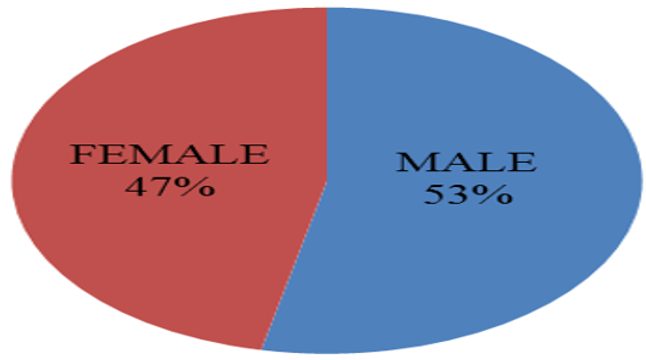
The rational antibiotic prescription is very important to prevent antimicrobial resistance. Widespread use of antibiotics has facilitated the development of resistance. The main aim of the study is to evaluate the use of antibiotics in pediatric patients in a tertiary care hospital. A prospective observational analysis of 283 case sheets of pediatric patients was done using medical records for six months. Data was collected on data collection forms from the patients who satisfy the inclusion criteria. Data were analyzed for Age distribution, Gender distribution, No. of antibiotics prescribed, Combinational drugs, Route of administration, Drug Interactions. Data were analyzed by using suitable statistical methods and expressed as pie charts, bar diagrams & tabular columns. In our study, we found that means the age of the pediatric patient was 2.72, average no of antibiotics per prescription was 1.1, Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid is frequently used, β- lactam class of antibiotics are commonly used. Antibiotic resistance is an emerging problem worldwide which can be controlled by rational prescribing, restricting the no of antibiotics per prescription and appropriate selection of drug. Here our study follows rational use of antibiotics.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.