Abstract
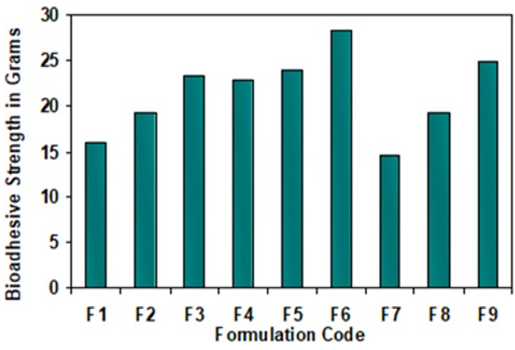
Controlled release gastro-retentive drug delivery systems offer many ad- vantages for drugs having local action in the stomach or upper part of the gastrointestinal tract and control their release in the proximal part of GIT and improve their bioavailability. The objective of this study was to formulate mucoadhesive tablets to enhance the gastric residence time of the drug Nizatidine for the management of peptic ulcer. Nine prototypes, controlled release mucoadhesive tablet formulations were designed using the mucoad- hesive polymer Carbopol 934P in combination with swellable polymers HPMC K4M, Polyox WSR303 and Xanthan Gum in different concentrations. The tablets were prepared by a direct compression method. The formulated tablets were evaluated for different quality parameters including in-vitro dissolution and diffusion study, in-vitro bioadhesion strength, drug content. The cumulative percentage drug release data revealed that formulations F2, F4 and F9 were highly effective in retarding drug release up to 12 hrs with 99.863%, 99.657%, 99.384% release respectively. The release mechanism explained with 5 models viz: zero order, first order, Higuchi and Peppa’s. The overall drug release was observed to follow zero order kinetics and data obtained fitted well with the Higuchi’s equation following non-fickian diffusion mechanism. The bioadhesive strength was found to be the function of nature and concentration of polymer used. Stability study performed for a month (40°C±2°C/75%±5%RH) exhibited no variations. The mucoadhesive gastroretentive formulation could be a promising delivery system for Nizatidine with the controlled release and promote local delivery of the drug to its site of action in the upper GIT.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.