Abstract
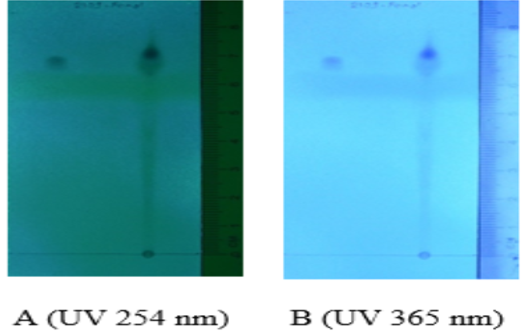
Jeruju has the potential as a source of bioactive components. Steroids are commonly found in mangroves, especially in the mangrove leaves (Acanthus Illicifolius) or better known as jeruju plants. However, the use of mangroves in Indonesia as a medicinal plant is still very limited. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the bioactive components of mangrove plants. The purpose of this study was to determine the active content of jeruju leaves (Acanthus Illicifolius) as an analgesic with the Gas Cromatographic Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis method. The design of this study was experiments with the stages are sampel preparation, extraction and fractionation and GC-MS analysis. The results of the Acanthus Illicifolius study contain protein, carbohydrate, saponin, sterooid, triterpenoids, and phenol. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) results showed that the compound separation was evidenced by the presence of spots as a result of elution with the detection of ferric chloride spray at UV 254 nm and 365 nm. Blotches eluted fluorescently on UV 365 nm with spot colors of phenolic compounds in visible black gray with phenol Rf detected 0.85. At the retention time of 40.22 to 43.89 minutes, there were 3 peaks of a large chromatogram and indicated the presence of topiramate, budesonide, and spingosine.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.