Abstract
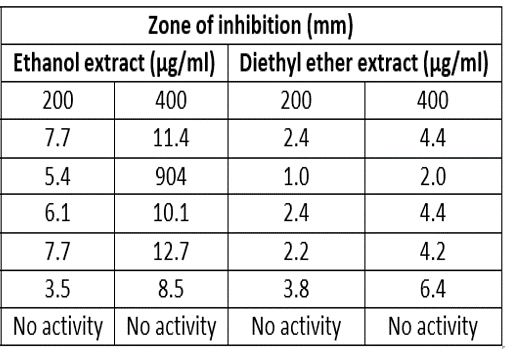
In vitro studies on antibacterial activity of organic extracts (Diethyl ether and Ethanol) of two medicinal plants Aloe barbadensis L and Lawsonia inermis L were carried out against three common human pathogenic (Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus and E.coli) bacteria. Both the two types of extracts of Lawsonia inermis showed antibac- terial activity on three types of bacteria, where as Aloe barbadensis extracts showed antibacterial activity on S. aureus, B. subtilis and not on E. coli bacteria. The diameters of zone of inhibitions of two types of extracts of two plants were also varied. Between the two types of organic extracts of two plants, Ethanol extracts showed more antibacterial activity than Diethyl ether extracts. Zones of inhibition were comparatively high in case of ethanol extracts of both plants than diethyl ether extracts.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.