Abstract
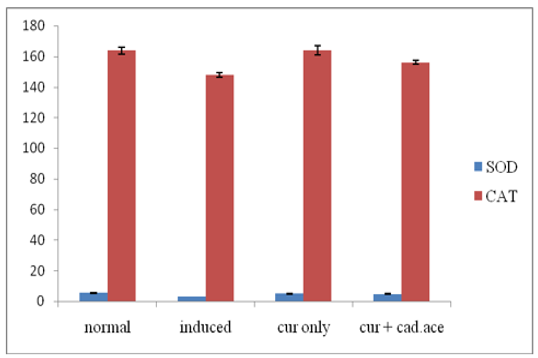
Pollution is a worldwide environmental problem that affects our environment in a wide range. These pollutants causes a great variety of health problems. Among them, toxic metals play an important role. The one comnmon toxic metal is cadmium. Curcumin (diferuoyl methane) is a well-knowm biologically active compound in tumeric derived from the rhizome of plant curcuma longa . curcuma longa is a gold coloured spice most commonly used in food as colouring agent and also for preservation of food. The aim of our present study was to evaluate the toxici- ty nature of cadmium acetate and antioxidant capacity of curcumin on liver injury in albino mice. The animals were randomly divided into four groups, each with six animals. Group I (control group) received normal feed, Group II was administered with cadmium acetate (200 mg/kg) dissolved in water, Group III was administered only with curcumin and Group IV received a dose of 250 mg/kg of curcumin and 200 mg/kg of cadmium acetate. The experiment was conducted for the period of 7 days. Rats treated with cadmium acetate alone showed a increased activity of ALT, AST and a decreased activity of ALP, Protein concentrartion in serum. And also a marked decline in antioxidant enzymes like Superoxide dismutase and Catalase in cadmium acetate induced rats. However, on com- bined treatment of rats with curcumin and cadmium acetate provoked the above changes more significantly, when compared to each of them as alone. Hence it is suggested that curcumin has a protective effect against a cadmium acetate induced hepatic injury.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.