Abstract
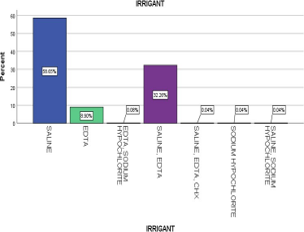
Pulpectomy is a procedure done for non-vital teeth which involves the extirpation of pulp from primary teeth and filling it with an inert substance. pulpectomy requires biomechanical preparation, but this biomechanical preparation alone is insufficient. Irrigants are used during this procedure for the purpose of lubrication, disinfection and washing away action. These irrigants penetrate the smaller accessory and lateral canals, thereby cleaning and disinfecting them. It is essential to eradicate the microorganisms and their by products from the root canal and pulp chamber. The collected data was further analyzed, recorded in Microsoft excel software and was subjected to statistical analysis using IBM SPSS statistics analyzer. The total sample size of the current study was 2400 cases. The most common age group of the patients who reported to the clinics were 0 to 5 years of age (69.1 %) (p < 0.05 - significant). The more common gender for using saline as an irrigant were male (57.7 %) (p < 0.05 - significant). We found that saline was the most commonly used irrigant (58.7 %), while sodium hypochlorite was the least commonly used (0.1 %). The most common visit for using saline as an irrigant were single visit (p < 0.05 - significant) followed by multi-visit. Within the limitations of the current study, saline was the most commonly used and sodium hypochlorite was the least commonly used for pulpectomy procedure in primary teeth. Saline was also commonly preferred for single visit in patients in the age group of 0 to 5 years.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.