Abstract
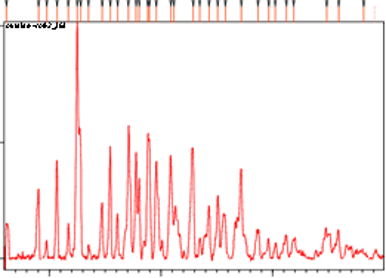
Gliclazide and β-cyclodextrin (Gli/β-CD) dispersions were prepared with a view to study the influence of β-CD on the solubility and dissolution rate of this poorly soluble drug. Phase-solubility profile indicated that the solubility of gliclazide was significantly increased in the presence of β-cyclodextrin and was classified as AL-type, indicating the 1:1 stoichiometric inclusion complexes. Physical characterization of the prepared systems was carried out by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffraction studies (XRD) and IR studies. Solid state characterization of the drug β-CD binary system using XRD, FTIR and DSC revealed distinct loss of drug crystallinity in the formulation, ostensibly accounting for enhancement of dissolution rate. The drug release from solid dispersion obeyed first order kinetics. Solid dispersions of gliclazide exhibited a 14 times fold increase in dissolution rate over pure drug.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.