Abstract
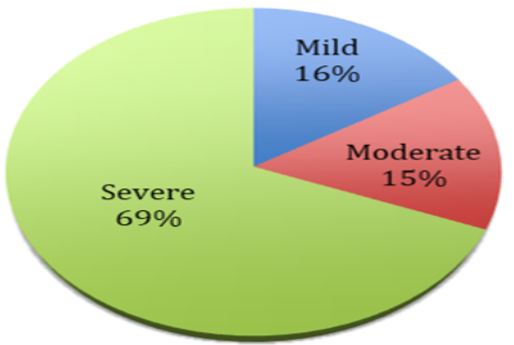
Chronic periodontitis is the second most common oral disease worldwide. It is a multifactorial disease with a bacterial plaque as the necessary factors; however, other factors such as age, systemic conditions and social habits do play a determining role in the development of periodontitis. Therefore, this study evaluated the correlation between the severity of chronic periodontitis with a series of socio-demographic background and clinical variables. This was a retrospective, observational study of chronic periodontitis population that attended IIUM Dental Clinic from the year 2014 to 2017. The data was extracted from patients’ case records systematically using structured data extraction form. Only case records with full clinical history and periodontal charting were undertaken as samples. IBM SPSS-24 was used for data analysis. Chi-square (χ2 ) and Mann-Whitney U tests were applied to infer the above relationship. Those who are professional workers, suffered from systemic diseases and were addicted to tobacco exhibited more severe disease, though statistically not significant. Patients with moderate and severe chronic periodontitis showed greater plaque deposits and had deeper periodontal pockets than those with mild form (p<0.05). Severe chronic periodontitis was found prevalent in the studied population. As a conclusion, the clinical and socio-demographic characteristics showed non-significant correlations with the severity of the disease except for gender, plaque control levels, and a number of deep pocket sites. Future studies should consider including more sample size from multicenter population.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.