Abstract
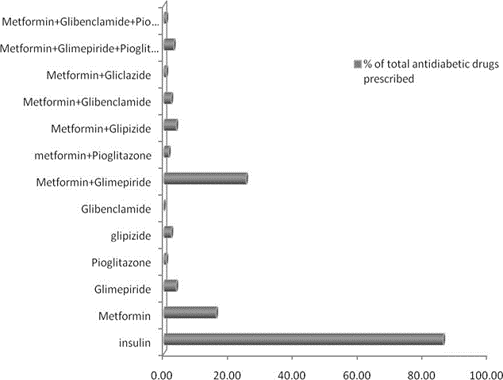
The guidelines for the treatment of type 2 diabetes have increasingly favored tighter glycemic control, necessitating the use of more aggressive pharmacological therapy. The objective of this study was to describe trends in the prescription of anti-diabetic medications among in-patients with type 2 diabetes. The study included 130 patients who had diabetes mellitus 2, were of either sex, any age, and had been undergoing treatment at tertiary care teaching hospital, Bangalore. A data was compiled from the medication usage records maintained by the hospital. Data were analyzed using SPSS 13.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, United States of America). Student's t-test and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were employed to compare quantitative variables, and the chi-square test was applied to compare categorical variables. Results indicate that 58.46% of the study population was male patients, out of which 55.26% were having history of either smoking or alcohol. The prevalence of diabetes was observed more in the population taking non-vegetarian diet. Most common disease associated with diabetes mellitus was found to be hypertension (45.38%). Highest prevalence of disease was found to be in the age group of 51 to 60 yrs (28.46%). Highest prescribed antidiabetic agent is insulin followed by metformin and then glimepiride. In combinational therapy metformin and glimepiride is the maximum prescribed combination. The study indicated that the choice of anti-diabetic drugs remained more or less unchanged compared to previous studies. The study also revealed the common use of metformin and glimepiride along with insulin treatment for inpatients. The study pro- vides baseline data for carrying out further therapeutic audit with more parameters of analysis which in turn will provide regular feedback to researchers and prescribers. This may encourage rational prescribing in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.