Abstract
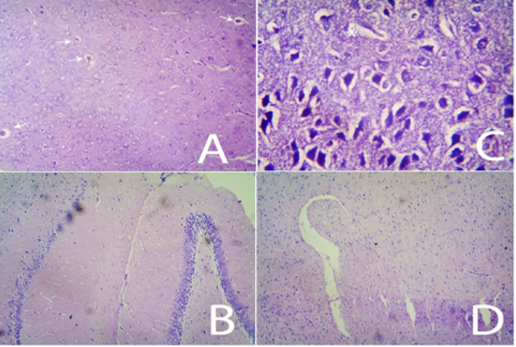
Angiotensin-converting enzymes are increasingly being tested in therapeutics of Parkinsonism. The objective of the present study was to evaluate the behavioral changes and neuroprotective role of captopril in the rotenone model of Parkinsonism in rats. Adult Wistar albino rats were divided into four groups of six each. Parkinsonism was induced with rotenone (3 mg/Kg intraperitoneal) in three groups. The experimental group was treated with captopril (20 mg/kg intraperitoneal). The effects were compared with a standard group treated with levodopa (12 mg/Kg) and Benserazide (3 mg/Kg). Behavioral effects were evaluated by the rotarod test, spontaneous locomotor activity, hole board test, forced swim test, and tail suspension test. Neuroprotection was noted with an estimation of glutathione and lipid peroxidation from rat brain homogenate. Levels of dopamine, serotonin, and GABA were also noted. Haematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of the brain evaluated for any histoarchitectural changes. Rats pre-treated with captopril have shown a significant increase in the duration of stay in the rotarod test, a significant increase in the number of head dipping in hole board test, significant lower duration of immobility in forced swim test and tail suspension test. Captopril has shown significant improvement in motor coordination (as evidenced through rotarod test), exploratory behavior (hole board test), depression (forced swimming test, and tail suspension test). Captopril significantly reduces oxidative stress conditions. Captopril has not shown major histoanatomical changes in the rotenone model. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; neuroprotection; dopaminergic neurons; Parkinsonism; rotenone model
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.