Abstract
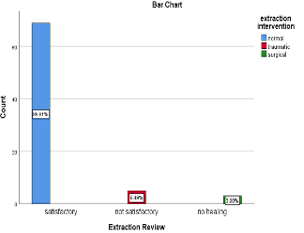
Diabetes is a common metabolic disorder which is an inability to regulate blood glucose due to insulin deficiency or resistance. During extraction, diabetic patients suffer various complications. One among them is most commonly seen delayed wound healing. The aim of this study is to evaluate the prevalence of delay in the healing process of extraction sockets in diabetic patients. This retrospective cross-sectional study was carried out in a hospital setting where all case sheets for six months were filtered from the patient management software. Samples of all patients with diabetes and the extraction treatment were filtered. Three hundred sixteen patients were used for this study. The data is collected and imported to SPSS for statistical analysis and results are obtained. Among 316 patients, 77 were diabetic and had undergone extraction treatment. Satisfactory healing was observed in diabetic patients undergoing normal extraction within the age group 60-70 years and with blood glucose level within normal range (54%). Unhealed sockets were observed in diabetic patients who underwent surgical extraction within the age group of 60-70 years and with high blood glucose level (10.2%). Majority of patients with normal blood glucose level have satisfactory healing and patients with high blood glucose level have unhealed sockets. Dentists should be aware that diabetic patients of poor glucose control undergoing traumatic extraction are prone to delayed healing processes which lead the patient to discomfort and infections. Patients should be advised to have a proper diet and controlled level of glucose to prevent oral complications.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.