Abstract
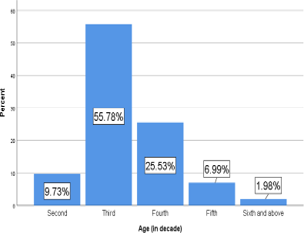
Mandibular third molar is the most commonly impacted teeth and surgical removal of them is the most common minor oral surgical procedure done under local anesthesia in the outpatient department. For a comfortable patient experience and best surgical results, emphasis should be made on a pain-free procedure. In this study, we aim to analyse retrospectively the amount of local anesthetic solution used during surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molar and to find if any association between the amount of local anesthesia used and Pederson's difficulty Index (PDI) of the impacted teeth. Retrospective observational study conducted among patients reporting to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Chennai for the surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molar between the study period June 2019 to March 2020. 658 patients who fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria were included in the study. Data regarding patients demography, site of impaction, Pederson Difficulty Index of impacted teeth, amount of local anesthesia used were rewarded. The data were statistically analysed using descriptive statistics in IBM SPSS version 20 software. Study population included 58.4% males and 41.6% females, majority of them in the 3rd decade of life. (53.6%) with mean age 29.1 years. Of 658 impacted teeth analysed 54.4% were moderately difficult followed by minimally difficult 38.4% and very difficult 7.1% according to PDI. A significant association was found between the amount of local anesthesia used and PDI score of impacted teeth. In 64.7% cases 2ml of local anesthesia was sufficient to achieve anesthesia during the procedure. 2ml of local anesthesia is sufficient to achieve adequate anesthetic effect in surgical removal of impacted molar. As PDI increased, the amount of local anesthesia used also increased.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.