Abstract
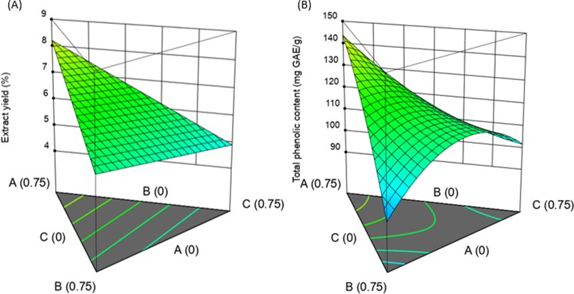
Cardamom (Amomum compactum Sol. Ex Maton) is a medicinal plant that belongs to the family Zingiberaceae. Phenolic compound detected in Cardamom fruit that responsible for several pharmacological activities. Optimization used the simplex centroid design for the yield and phenolic extractions of Cardamom fruit through maceration to optimize the mixing of water, acetone, methanol, and ethanol. The extraction yield is determined by weighing the extracted material compared to the whole sample. Total phenolic content was measured by a spectrophotometric method using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. The results show that the best for relating extract yield is the linear model, while the quadratic model is the best to connect total phenolic content response. Water (100%) solvent extraction on Cardamom fruits obtained the highest extract yield (10.52%) and the lowest extract yield from 100% ethanol. The extraction of phenolic compounds with a mixture of water (50%)/ethanol (50%) resulted in maximum total phenolic content (168.98 mg GAE/g). However, the 100% ethanol of solvent extraction noted the minimum phenolic content (93.15 mg GAE/g). The results show that we should carefully choose the solvent mixture extraction to achieve the extract yield and phenolic extraction goals. This study first reported an optimization study on phenolic compounds extracted from Cardamom fruit.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.