Abstract
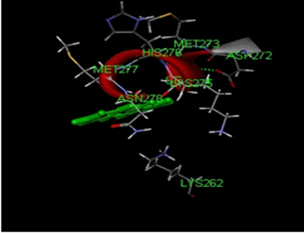
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder. Phosphodiesterase is a family of 1-11 among which PDE4 is most predominant enzymes present in inflammatory cells. Commercially available drugs are synthetic, and these may cause various side effects and are expensive. Dimethyl fumarate is the most frequently used systematic treatment for psoriasis with significant side effects such as myelosuppression, hepatic fibrosis and pulmonary fibrosis. Immune compromise drugs having various side effects, so this project is aimed to propose a novel drug that has more potency, efficiency and least side effects. The docking analysis was carried out to identify the best ligands by predicting the ligand conformation in the active protein sites and ligand binding affinity towards protein. Ligands were docked with the proteins, and all exhibited higher docking score than the standard drug dimethyl fumarate. The TNF- α inhibitors with PDB id such as 2ZJC, 2ZPX and PDE4 Inhibitors with PDB ID such as 3SL3, 1PTW are selected as target proteins, acridone had the best docking score of 19.3502 than standard value 12.997, and with PDB ID 3SL3, acridone showed 26.025 as docking score over the standard value 21.995. it interacted well with the active sites of the proteins. Thus, we infer that these studies will be a leader, in designing new and improved drug target for psoriatic therapy.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.