Abstract
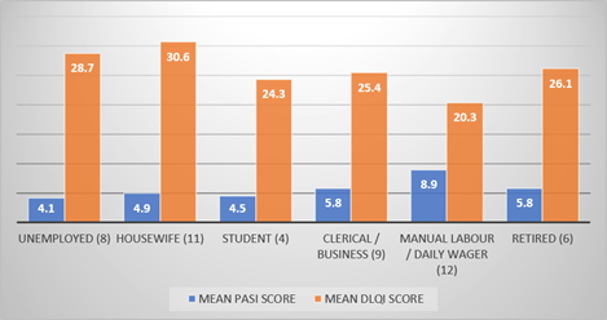
Psoriasis is a common chronically relapsing auto-inflammatory disease of the skin affecting patients of all ages and both genders. There is a more significant impact on the quality of life in patients with established disease. The study was conducted to correlate the relation between dermatology life quality index and psoriasis area and severity index and thereby deriving the impact of one on the other. This is a cross-sectional, descriptive study undertaken in psoriasis patients who had disease manifestations but did not undergo any treatment. Patient’s DLQI and PASI were calculated at a given point of time. Fifty patients participated in the study. Thirty-three patients were men, with a mean age of 37 years, and seventeen patients were women with a mean age of 34 years. PASI & DLQI were tabulated and compared with age, gender, disease duration, occupation etc. PASI is a reliable parameter to measure the severity of disease and DLQI for measuring the quality of life in psoriatic patients. PASI and DLQI are reliable parameters, and combining both and correlating them with various demographic and lifestyle parameters gives a clear indication of how these influence the disease impact in general.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.