Abstract
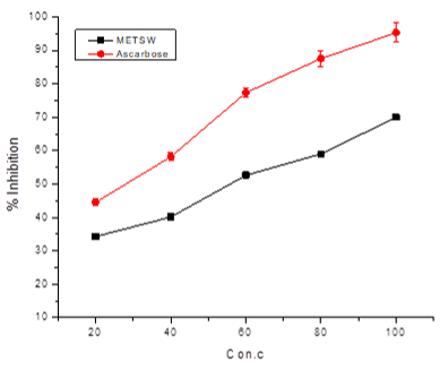
Tradescantia spathacea Swartz belongs to the genus Commelinaceae, a tropical tree used in many countries as an herbal drug for the care of diabetic patients. The aim of this study was to examine anti-diabetic activity of the Tradescantia spathacea Swartz methanolic extract (METSW) and the in-vitro activity of α-amylase, and α-glucosidase was carried out. METSW compared with acarbose inhibition of the α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzyme, METSW exhibited IC50 less than 100µg/mL would be considered as healthy. The METSW showed IC50 66.22 ± 0.52µg/mL α-amylase activity, acarbose revealed an IC50 of 83.25 ± 1.28µg/mL. METSW demonstrated IC50 levels of 85.37 ± 0.72 µg/mL (y= 0.095x+41.89) inhibition of the α-Glucosidase enzymes. METSW at 400 mg/kg greatly decreased the region under the blood glucose level curve in a typical rat test for oral glucose tolerance. The single dose of the extract decreased dramatically from 211 mg/dl to 89.22 mg/dl at 400 mg/kg METSW in the alloxan induced diabetic model. METSW possesses strong antidiabetic activity in vivo and in vitro. Besides, the extract has also been shown to have a significant inhibitory activity of α-amylase and α- glucosidase which may lead to its anti-hyperglycemic function when used in diabetic patients.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.