Abstract
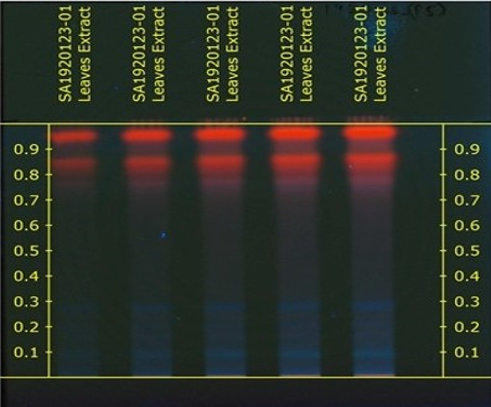
This present study involves the assessment of the anti-oxidant activity study of the sample which was obtained from the methanolic extracts of dried leaves of Portulaca Oleracea L.(common name Purslane). Purslane is a rich source of Vitamin A, Vitamin-C and some other B-complex vitamins like riboflavin, niacin, pyridoxine and carotenoids which are known powerful natural antioxidants. Anti-oxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation. This methanolic extract of leaves was evaluated for the determination of its anti-oxidant efficiency by using 1,1–diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) by using Silica TLC plates on Camag High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) system using visionCATS software. Densitograms and chromatographs obtained show the presence of anti-oxidant activity. It is a rapid, inexpensive and straightforward method to measure anti-oxidant properties of substances after separation by HPTLC. It involves the use of the free radical, 2, 2-Diphenyl- 1- picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) which is widely used to test the ability of compounds to act as free radical scavengers or hydrogen donors and to evaluate antioxidant activity. When Anti-oxidants substances react with DPPH, which is a stable free radical becomes paired off in the presence of a hydrogen donor (e.g., a free radical scavenging anti-oxidant) and is reduced to the DPPHH. As a consequence, the absorbance’s decreased from the DPPH.
Full text article
References
Alam, M. A., et al. 2014. Evaluation of Anti-oxidant Compounds, Anti-oxidant Activities, and Mineral Composition of 13 Collected Purslane (Portulaca Oleracea L.) Accessions. BioMed Research International, page 10. Article ID 296063.
Chowdhary, C. V. 2013. A Review on Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profile of Portulaca Oleracea Linn. (Purslane). International Journal of Research in Ayurveda and Pharmacy, 4(1):34–37.
Dkhil, M. A., et al. 2011. Anti-oxidant Effect of Purslane (Portulaca Oleracea) and Its Mechanism of Action. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 5(9):1589–1563.
Erkan, N. 2012. Anti-oxidant Activity and Phenolic Compounds of Fractions from Portulaca Oleracea L. Food Chemistry, 133(3):775–781.
Hefnawy, T., Ali, O. 2015. Assessment of antioxidant capacity of ethanolic extract of Portulaca oleracea leaves in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 9(10):335–342.
Iranshahy, M., Javadi, B., Iranshahi, M., Jahanbakhsh, S. P., Mahyari, S., Hassani, F. V., Karimi, G. 2017. A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Portulaca oleracea L. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 205:158–172.
Naeem, F., Khan, S. H. 2013. Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) as Phytogenic Substance—A Review. Journal of Herbs, Spices & Medicinal Plants, 19(3):216–232.
Nile, S. H. 2017. Total Phenolics, Antioxidant, Antitumor, and Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of Indian Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Extracted with Different Extraction Methods. 3 Biotech.
Rahimi, V. B. 2018. A Pharmacological Review on Portulaca Oleracea L.: Focusing on Anti Inflammatory, Anti-Oxidant, Immuno-Modulatory and Antitumor Activities. Journal of Pharmacopuncture, 22(1):7–15.
Sanja, S. D., et al. 2009. Characterization and Evaluation of Anti-oxidant Activity of Portulaca Oleracea. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1(1).
Sicari, V., et al. 2018. Portulaca Oleracea L. (Purslane) Extracts Display Antioxidant and Hypoglycaemic Effects. Journal of Applied Botany and Food Quality, 91.
Simopoulos, A. P., Norman, H. A., Gillaspy, J. E., Duke, J. A. 1992. Common purslane: a source of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 11(4):374–382.
Uddin, M. K., et al. 2014. Purslane Weed (Portulaca Oleracea ): A Prospective Plant Source of Nutrition, Omega-3 Fatty Acid, and Anti-oxidant Attributes. The Scientific World Journal. Article ID 951019.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.