Abstract
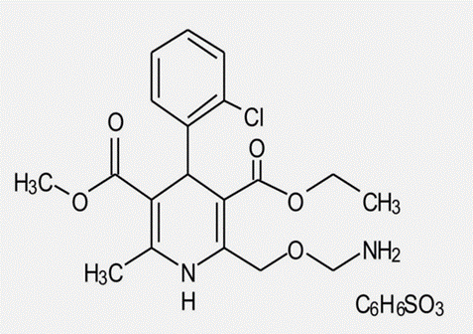
The oxidation of the pharmaceutical drug Amlodipine besylate [AML] by N-Bromosuccinimide [NBS] was investigated aqueous acidic medium under pseudo-first-order condition. The experimental results indicated that the reaction exhibits first-order concerning N-bromosuccinimide, fractional order concerning [AML] and sulphuric acid [H2SO4]. There was no substantial effect on the rate of the reaction with KNO3. The reaction stoichiometry shows one mole of amlodipine besylate consumes one mole of n-bromosuccinimide. The effect of temperature on the reaction rate was studied, and the activation parameters (Ea, △G, △H and △S) are calculated and tabulated. LC-MS technique was used to identify the oxidation product of amlodipine besylate. Based on experimental results, a mechanism is proposed, and constants K1, K2 and k3 involved in the mechanism were evaluated. The observed rate constant values and the experimental value calculated by substituting the value of k3= 4.0 × 10−3 s −1, K2 = 1272 moldm-3s−1 and K1= 1.96 x 10−6 in the rate equation is in good accordance with each other.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.